Operations Management
Operations management focuses on carefully managing the processes to produce and distribute products and services. Major, overall activities often include product creation, development, production and distribution. (These activities are also associated with Product and Service Management.) Related activities include managing purchases, inventory control, quality control, storage, logistics and evaluations of processes.
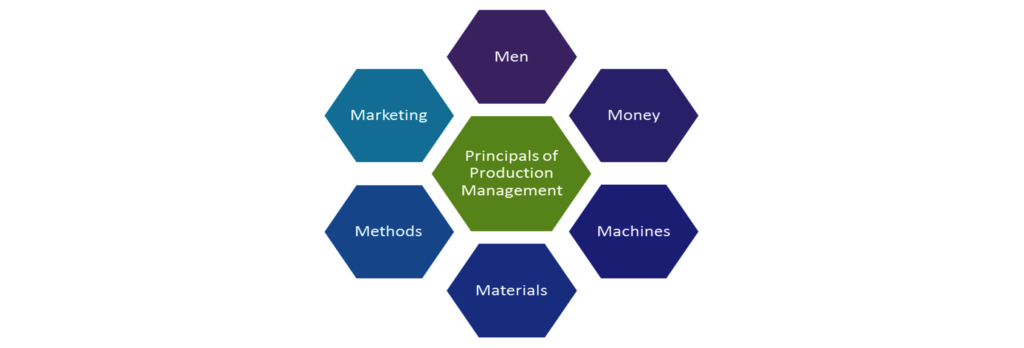
Production management means planning, organising, directing and controlling of production activities. Production management deals with converting raw materials into finished goods or products. It brings together the 6M’s i.e. men, money, machines, materials, methods and markets to satisfy the wants of the people. Production management also deals with decision-making.
The main objective of production management is to produce goods and services of the right quality, right quantity, at the right time and at minimum cost. It also tries to improve the efficiency. An efficient organisation can face competition effectively.
Process management is the ensemble of activities of planning and monitoring the performance of a business process. The term usually refers to the management of business processes and manufacturing processes. Business process management (BPM).Process management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools, techniques and systems to define, visualize, measure, control, report and improve processes with the goal to meet customer requirements profitably. Promotes the adoption of a process approach when developing, implementing and improving the effectiveness of a quality management system, to enhance customer satisfaction by meeting customer requirements.
Supply chain management (SCM), the management of the flow of goods and services, involves the movement and storage of raw materials, of work-in-process inventory, and of finished goods from point of origin to point of consumption. Interconnected or interlinked networks, channels and node businesses combine in the provision of products and services required by end customers in a supply chain. Supply-chain management has been defined [as the “design, planning, execution, control, and monitoring of supply chain activities with the objective of creating net value, building a competitive infrastructure, leveraging worldwide logistics, synchronizing supply with demand and measuring performance globally.
Reliability engineering is engineering that emphasizes dependability in the life-cycle management of a product. Dependability, or reliability, describes the ability of a system or component to function under stated conditions for a specified period of time.Reliability engineering is engineering that emphasizes dependability in the life-cycle management of a product. Dependability, or reliability, describes the ability of a system or component to function under stated conditions for a specified period of time.
Logistics is generally the detailed organization and implementation of a complex operation. In a general business sense, logistics is the management of the flow of things between the point of origin and the point of consumption in order to meet requirements of customers or corporations. The resources managed in logistics can include physical items such as food, materials, animals, equipment, and liquids; as well as abstract items, such as time and information. The logistics of physical items usually involves the integration of information flow, material handling, production, packaging, inventory, transportation, warehousing, and often security.
It seeks to improve the quality of the output of a process by identifying and removing the causes of defects and minimizing variability in manufacturing and business processes. It uses a set of quality management methods, mainly empirical, statistical methods, and creates a special infrastructure of people within the organization who are experts in these methods. Each Six Sigma project carried out within an organization follows a defined sequence of steps and has specific value targets, for example: reduce process cycle time, reduce pollution, reduce costs, increase customer satisfaction, and increase profits.
The fact or process of ensuring that appropriate amounts of stock are maintained by a business, so as to be able to meet customer demand without delay while keeping the costs associated with holding stock to a minimum. Inventory control or stock control can be broadly defined as “the activity of checking a shop’s stock”. More specifically inventory control may refer to: In operations management, logistics and supply chain management, the technological system and the programmed software necessary for managing inventory.
ISO 50001:2011 Energy management systems – The standard specifies the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining and improving an energy management system, whose purpose is to enable an organization to follow a systematic approach in achieving continual improvement of energy performance, including energy efficiency, energy security, energy use and consumption. The standard aims to help organizations continually reduce their energy use, and therefore their energy costs and their greenhouse gas emissions. A significant feature in ISO 50001 is the requirement to “…improve the EnMS and the resulting energy performance”. Both require improvement to the effectiveness of the Management System but not to quality of the product/service. In fact, improve quality and environmental performance, but the Standards do not specify it as a requirement
Hazard analysis and critical control points or HACCP is a systematic preventive approach to food safety from biological, chemical, and physical hazards in production processes that can cause the finished product to be unsafe, and designs measurements to reduce these risks to a safe level.
A core definition of Total quality management (TQM) describes a management approach to long–term success through customer satisfaction. In a TQM effort, all members of an organization participate in improving processes, products, services, and the culture in which they work. Quality Control is a product focused concept, where checking of the actual results are done to ensure that things are as expected. If the correct controls are in place you can know for certain that the actual results have been achieved because the actual results have been checked.
Statistical process control (SPC) is a method of quality control in which statistical methods are employed. SPC is applied in order to monitor and control a process. Monitoring and controlling the process ensures that it operates at its full potential. Statistical Process Control (SPC) is the term used to describe the set of statistical tools used by quality professionals. SQC is used to analyze the quality problems and solve them. Statistical quality control refers to the use of statistical methods in the monitoring and maintaining of the quality of products and services. Statistical process control (SPC) is a method of quality control which uses statistical methods. SPC is applied in order to monitor and control a process. Monitoring and controlling the process ensures that it operates at its full potential. At its full potential, the process can make as much conforming product as possible with a minimum (if not an elimination) of waste (rework or scrap)
5S is the name of a workplace organization method that uses a list of five Japanese words: seiri, seiton, seiso, seiketsu, and shitsuke. They all start with the letter “S”.The list describes how to organize a work space for efficiency and effectiveness by identifying and storing the items used, maintaining the area and items, and sustaining the new order. The decision-making process usually comes from lines about standardization, which builds understanding among employees of how they should do the work.
Kaizen Reduces Waste in areas such as inventory, waiting times, transportation, worker motion, employee skills, over production, excess quality and in processes. Kaizen Improves space utilization, product quality, use of capital, communications, production capacity and employee retention. Kaizen provides immediate results. Instead of focusing on large, capital intensive improvements, Kaizen focuses on creative investments that continually solve large numbers of small problems. Large, capital projects and major changes will still be needed, and Kaizen will also improve the capital projects process, but the real power of Kaizen is in the on-going process of continually making small improvements that improve processes and reduce waste.